How Chinese-Made Cars Are Shaking Up the EV World
The global electric vehicle (EV) market is witnessing a seismic shift, with Chinese-made cars at the epicenter. China’s aggressive push into the EV sector is reshaping the industry, driven by robust government policies, strategic international deals, and rapid technological advancements.
Here’s how China is becoming a dominant force in the EV world and what it means for the future.
Unprecedented Growth and Innovation
China has emerged as the largest producer and consumer of electric vehicles globally. In 2023 alone, China’s EV sales surged by 36.7%, reaching 8.3 million units and accounting for nearly 30.8% of total vehicle sales (#SixthTone). Leading companies like BYD, NIO, and Xpeng are not only dominating the domestic market but are also expanding their footprint globally.
Government Policies and Support
China’s government has played a major role in the EV industry through a mix of subsidies, tax incentives, and regulatory mandates.
Here are some key policies:
- Subsidies and Incentives:Until recently, the government offered substantial subsidies for both manufacturers and consumers, significantly reducing the cost of EVs. Although these subsidies have been phased out, they were crucial in jump-starting the industry (#SixthTone) (TechXlore).
- Tax Relief: EV buyers benefit from tax exemptions, including the vehicle purchase tax, which can be as high as 10% of the vehicle’s purchase price. This makes EVs more affordable and attractive to consumers (Bolt Earth).
- Regulatory Mandates: The New Energy Vehicle (NEV) mandate requires manufacturers to produce a certain percentage of low-emission vehicles. This regulation has propelled companies to innovate and increase their EV production (California Management Review).
Strategic International Expansion
Chinese EV makers are not just focusing on their home market; they are making significant inroads into international markets. Here are some notable examples:
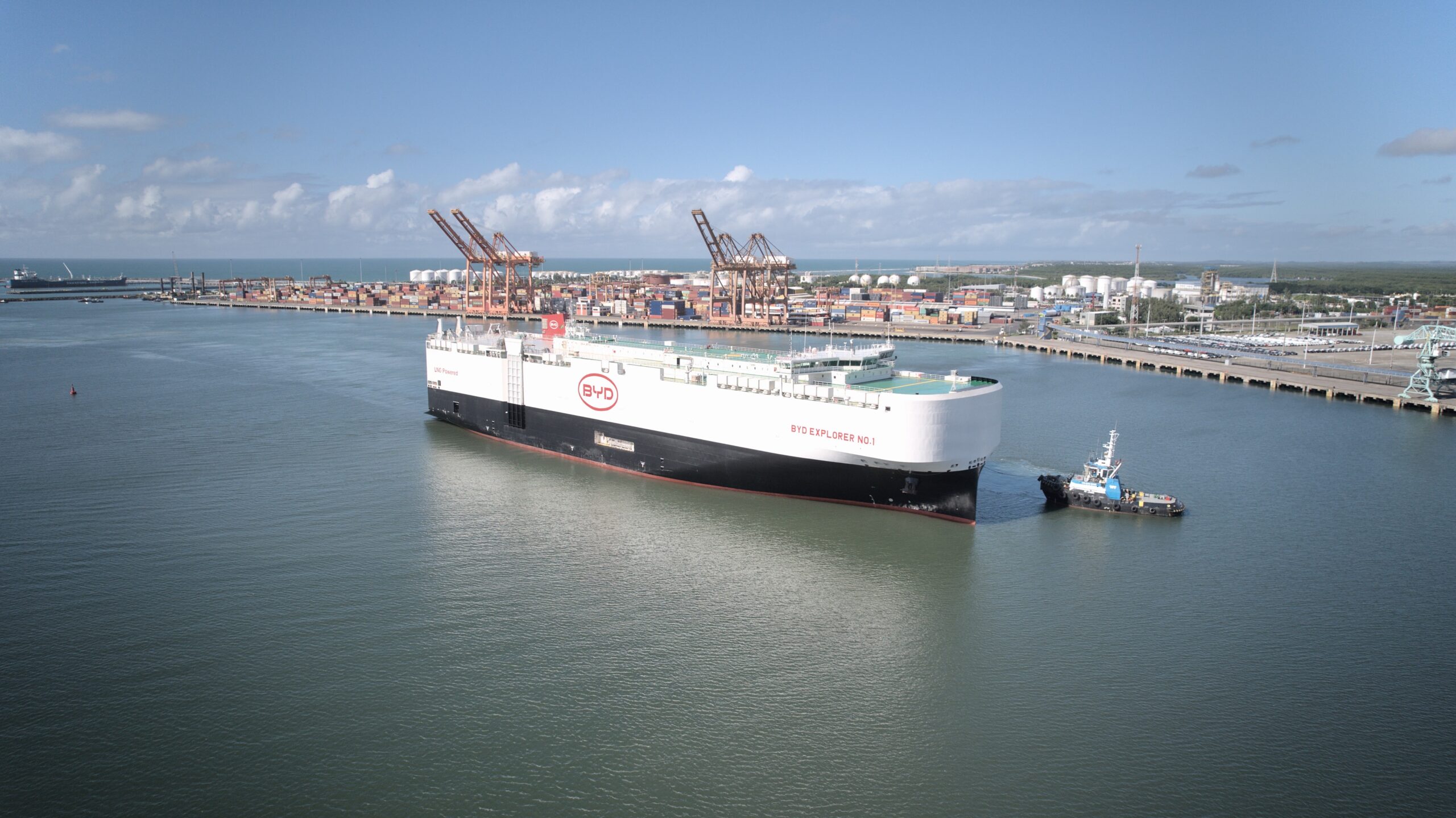
- BYD’s Global Push: BYD has expanded its presence in Europe, supplying electric buses and cars to various countries. In the first 11 months of 2023, China exported 4.4 million vehicles, marking a 58.4% increase from the previous year (#SixthTone) (TechXlore).
- NIO’s Battery Swap Stations: NIO is exporting its innovative battery swap technology to Norway, offering a unique solution to the charging infrastructure challenge and paving the way for further expansion in Europe (Counterpoint Research).
- Xpeng’s European Ventures: Xpeng has launched its G3 SUV and P7 sedan in Norway and is eyeing other European markets as part of its global strategy to compete with established brands like Tesla (Counterpoint Research).
Technological Advancements
Chinese companies are at the forefront of EV technology, investing heavily in research and development to enhance battery life, charging speed, and autonomous driving capabilities.
For example, Xpeng’s P7 sedan offers a range of up to 700 kilometers on a single charge, showcasing the technological prowess of Chinese EV makers (Bolt Earth).

Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their rapid growth, Chinese EV manufacturers face several challenges, including intense competition and the need to build brand trust in new markets.
The domestic market is also highly competitive, with price wars and the phasing out of subsidies squeezing profit margins (#SixthTone).
However, China’s dominance in the EV supply chain, including the control of critical raw materials like lithium and cobalt, provides a significant advantage. This control ensures a steady supply of essential components for EV production, mitigating some of the risks associated with global supply chain disruptions (California Management Review).
Conclusion
Chinese-made cars are undeniably shaking up the EV world. With strong government support, strategic international expansions, and a focus on technological innovation, Chinese automakers are expected to play a crucial role in the future of electric vehicles. As the industry evolves, the impact of these companies on the global market will be significant, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient transportation future.